WAN Encryption and Optimization
Are Your WANs under Siege?
- Remote users, cloud-based applications, and growing internet traffic are overwhelming legacy WANs.
- WANs need to be optimized to maintain QoS (Quality of Service) levels while ensuring data is protected across all WAN links.
- IT professionals strive to contain costs by optimizing their WANs and use encryption to keep their information secure during data transfer.
WAN Encryption and Optimization
Bring Processes Together
WAN encryption protects data while it’s traveling through a WAN infrastructure. WAN optimization ensures the WAN links are fully utilized.
- Load Balancing – Network load balancing, also known as multi-homing or dual-WAN routing, balances traffic across multiple network links.
- Traffic Shaping – Packet or traffic shaping delays traffic flow from low priority applications so that high priority traffic, such as OLTP, maintains the required quality of service. This is possible if the WAN has,
- Technology that monitors application and network loads
- Can analyze traffic to determine the application classification or custom applications
- Make intelligent decisions to delay traffic or reroute traffic to lower or higher-performing paths as needed
- Failover – In the rare event, a connection or device suffers a disruption, the WAN will automatically move the traffic to an alternative route. This ensures continuous access to critical applicators and maintains the quality of service.
WAN Encryption
Encryption is the process of encoding data. It converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative unreadable form known as ciphertext. Popular encryption engines such as AES 256 have proven nearly impossible to break. Data can be encrypted by software or hardware such as router encryption. The encryption process generates the unique key required to decrypt the data. Popular WAN encryption techniques include IPsec (L3), Optical Network (L1), MACsec (L2). WAN and broadband links/traffic should always be encrypted to ensure complete cybersecurity. As an example, cloud data encryption encrypts data before it is sent to a cloud.
WAN Optimization with Data Deduplication
Deduplication streamlines WAN throughput by filtering and ignoring copies of the same packet. Instead of transmitting multiple copies on the same packet, only one is sent. The packet header is inspected, and all fields must be identical. In some cases, headers may be altered slightly as the packet navigates through the network. Fine-tuning or deeper packet inspection may be required to find duplicates.
WAN Optimization with Data Compression
Compression looks within the data to find areas where the same data can be compressed in a more compact manner. This requires an explicit algorithm that is used to compress and decompress the data to its original form.
Other Optimization Techniques
In order to maintain QoS (Quality of Service), other optimization techniques can be used including,
Encryption is the process of encoding data. It converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative unreadable form known as ciphertext. Popular encryption engines such as AES 256 have proven nearly impossible to break. Data can be encrypted by software or hardware such as router encryption. The encryption process generates the unique key required to decrypt the data. Popular WAN encryption techniques include IPsec (L3), Optical Network (L1), MACsec (L2). WAN and broadband links/traffic should always be encrypted to ensure complete cybersecurity. As an example, cloud data encryption encrypts data before it is sent to a cloud.
Deduplication streamlines WAN throughput by filtering and ignoring copies of the same packet. Instead of transmitting multiple copies on the same packet, only one is sent. The packet header is inspected, and all fields must be identical. In some cases, headers may be altered slightly as the packet navigates through the network. Fine-tuning or deeper packet inspection may be required to find duplicates.
Compression looks within the data to find areas where the same data can be compressed in a more compact manner. This requires an explicit algorithm that is used to compress and decompress the data to its original form.
In order to maintain QoS (Quality of Service), other optimization techniques can be used including,
- Load Balancing – Network load balancing, also known as multi-homing or dual-WAN routing, balances traffic across multiple network links.
- Traffic Shaping – Packet or traffic shaping delays traffic flow from low priority applications so that high priority traffic, such as OLTP, maintains the required quality of service. This is possible if the WAN has,
- Technology that monitors application and network loads
- Can analyze traffic to determine the application classification or custom applications
- Make intelligent decisions to delay traffic or reroute traffic to lower or higher-performing paths as needed
- Failover – In the rare event, a connection or device suffers a disruption, the WAN will automatically move the traffic to an alternative route. This ensures continuous access to critical applicators and maintains the quality of service.
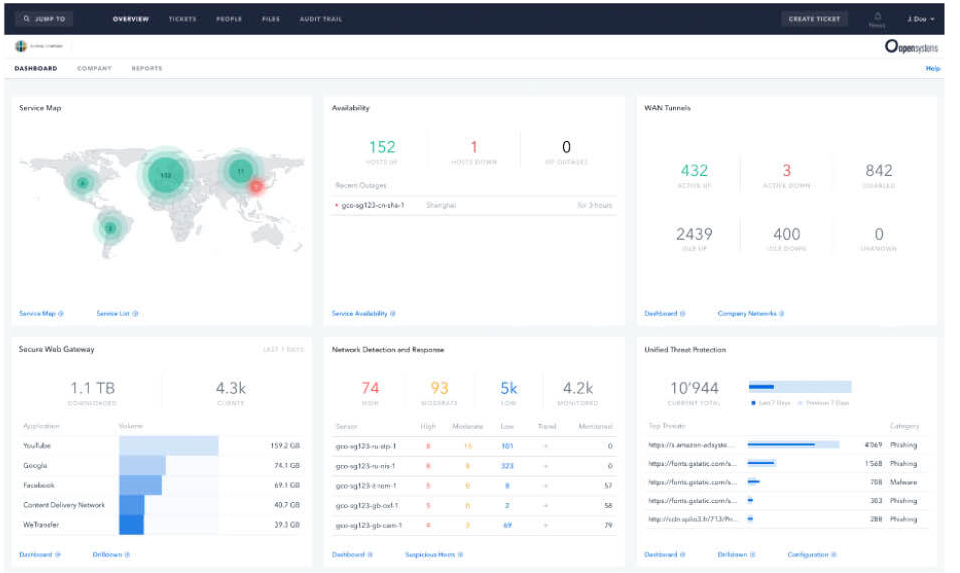
Our unified management console includes comprehensive network performance monitoring, control, optimization, and management across the entire network stack, from the core – to cloud – to edge.
In addition our MDR (Managed Detection and Response) service provides cybersecurity and intrusion detection. Services can include a full SOC (Security Operation Center) as-a-Service to support cyber threat containment and remediation.

The Benefits of Migrating to An SD-WAN
Network Optimization
Network optimization is one of the main benefits of migrating to an SD-WAN. SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN) is a service that overlays the hybrid network infrastructure. An intelligent software layer manages both MPLS WAN and other connections such as broadband and. It provides simpler management of the entire network. The SD-WAN continually monitors application performance and hybrid network traffic. The performance data is collected in real-time and used to intelligently determine and dynamically configure the best routes to meet or exceed service level requirements.
IP Network
In addition to traditional WAN links and SD WAN encryption, leading SD-WAN services offer an IP network, which it manages from end to end. IT professionals now have hundreds to thousands of PoPs (Points of Presence) all over the world. User traffic to the PoP is more manageable, higher performing, and more predictable than public internet connections. Moreover, cybersecurity and access control can be administered by the PoP as part of the SD-WAN service.
Traffic Routing
Unlike traditional WANs, the additional software layer monitors and reconfigures the network with minimal user intervention. Routing traffic is policy-driven and automatic. Traffic is no longer directed along a predetermined path but along the path that will ensure the prescribed quality of service. SD-WANs deliver the intelligence and agility needed to optimize network performance. SD-WAN technology overcomes the latency inherent in rigid legacy WANs to help IT professionals address the growing traffic generated by cloud applications and the internet.
Network optimization is one of the main benefits of migrating to an SD-WAN. SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN) is a service that overlays the hybrid network infrastructure. An intelligent software layer manages both MPLS WAN and other connections such as broadband and. It provides simpler management of the entire network. The SD-WAN continually monitors application performance and hybrid network traffic. The performance data is collected in real-time and used to intelligently determine and dynamically configure the best routes to meet or exceed service level requirements.
In addition to traditional WAN links and SD WAN encryption, leading SD-WAN services offer an IP network, which it manages from end to end. IT professionals now have hundreds to thousands of PoPs (Points of Presence) all over the world. User traffic to the PoP is more manageable, higher performing, and more predictable than public internet connections. Moreover, cybersecurity and access control can be administered by the PoP as part of the SD-WAN service.
Unlike traditional WANs, the additional software layer monitors and reconfigures the network with minimal user intervention. Routing traffic is policy-driven and automatic. Traffic is no longer directed along a predetermined path but along the path that will ensure the prescribed quality of service. SD-WANs deliver the intelligence and agility needed to optimize network performance. SD-WAN technology overcomes the latency inherent in rigid legacy WANs to help IT professionals address the growing traffic generated by cloud applications and the internet.
Migrating to a software-defined network is simple if your SD-WAN vendor has experience. We are the industry-leading experts in migrating networks to an SD-WAN.
Contact our customer advocates to learn how a managed SD-WAN can optimize performance while reducing management complexity and costs.

Leave Complexity
Behind
To learn how Open Systems SASE Experience can benefit your organization, talk to a specialist today.
Contact Us